Steps and tips: Recruiting apprentices
The procedure for recruiting apprentices may vary depending on the country context. The regulatory framework of a country prescribes the roles and responsibilities of stakeholders in the recruitment process.
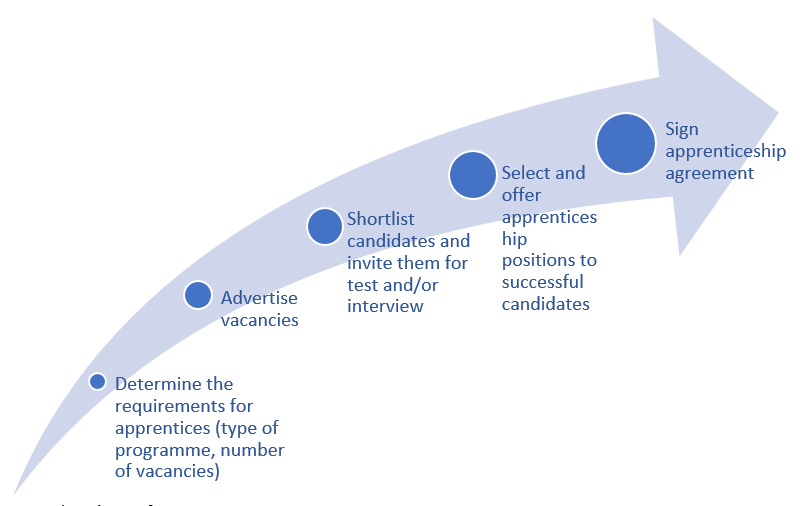
Enterprises may take the following generic steps for recruiting apprentices, as appropriate:
- Decide on the number of apprenticeships to be offered in various occupations, based on the company’s human resource needs and capacity to train apprentices in line with the applicable standards.
- Determine the remuneration and the training and working conditions for apprenticeships, based on the applicable standards.
- Openly advertise apprenticeship vacancies by different means, including through the enterprise’s website, social media, official websites of chambers, employers’ and workers’ organizations, as well as through schools and employment offices, to attract young people and reach the target recruitment pool.
- Prepare guidelines, including criteria for assessing the skills, knowledge and attitudes of candidates as well as their motivation for participating in apprenticeships.
- Conduct initial screening and shortlisting exercises, and invite candidates for tests and/or interviews.
- Following an interview, select and offer appointments to the successful candidate(s) and provide feedback to the unsuccessful candidates.
- Sign the apprenticeship agreement with the selected apprentice and register it with the competent body (refer to section "Formulating apprenticeship agreements").
Figure 5.1 Steps for recruiting apprentices for an enterprise
Source: Authors’ own figure.
TIPS
- Candidates for apprenticeships should be fully aware of the requirements of the chosen occupation so that they can make an informed decision when choosing a specific apprenticeship programme.
- Enterprises may invite students for a guided visit or offer a short work trial to potential candidates. In this way, students can become familiar with the programme and determine whether it meets their expectations, while employers have the chance to assess the suitability of potential candidates for apprenticeships.
- Enterprises may use different selection methods, such as aptitude tests, group discussions, role playing and work trials, to assess candidates’ suitability for apprenticeships.
- SMEs may seek support from intermediaries, TVET providers or public and private employment services in the selection process, as they may not have the necessary expertise for recruiting apprentices.
- TVET providers may cooperate with and support employers, while recognizing that employers should be entitled to select their own candidates.
- Enterprises may consider offering more favourable working conditions than those prescribed in order to attract better candidates.